Duolingo (DUOL) Company Overview
Duolingo is a US-based edtech company that delivers gamified language, math, music and chess learning via a mobile app and web platform. Its core product is a free, highly engaging language-learning app with optional paid subscriptions that remove ads and unlock premium features, including AI-powered tutoring. The company also operates the Duolingo English Test (DET), an online English proficiency exam accepted by thousands of universities worldwide. With over 100 courses in 40+ languages and more than 100 million monthly active users, Duolingo is the global category leader in digital language learning by user base.
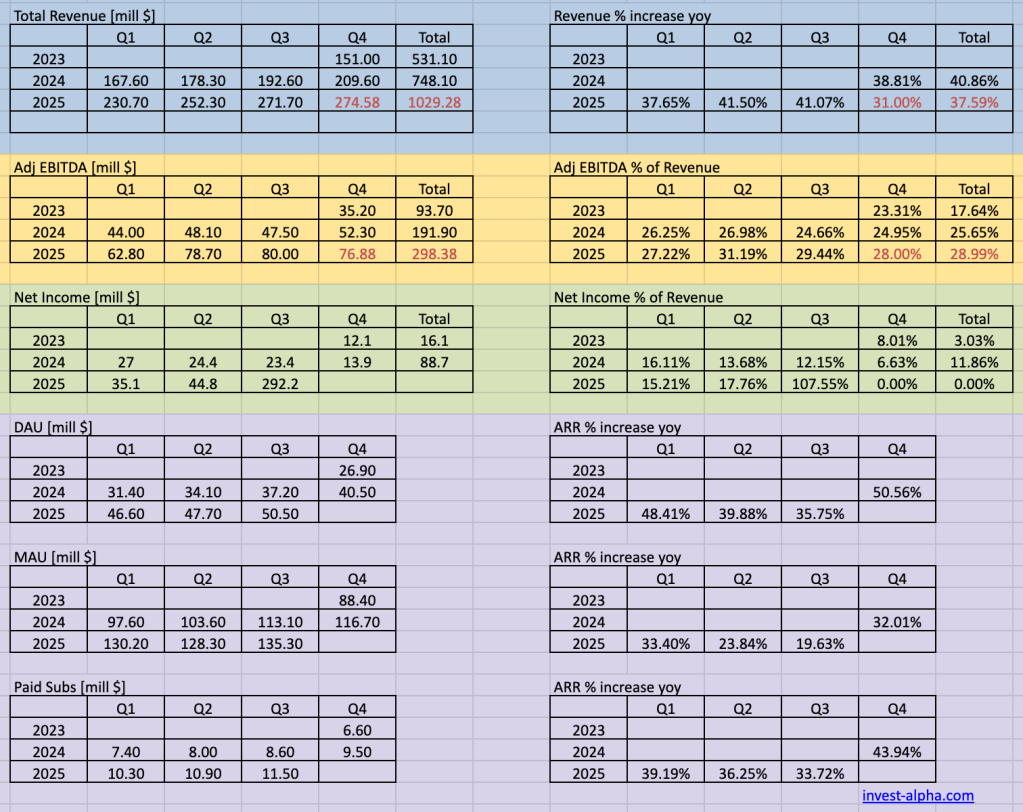
Duolingo Financial Performance and Key Metrics
Duolingo Bull Case: Why the Stock Could Outperform
- Category leader in a fast-growing market
- Duolingo is the most-used language-learning app globally and a leading brand in digital education, benefiting from a structural shift to online learning.
- Stock has been hit by concerns around tools like ChatGPT replacing Duolingo for language learnings. But the key value prop for Duoling is their ability to keep the user engaged through their game like interface that ensures engagement over a long period of time. Additionally they have course content that spans several years unlike what can be generated by tools like ChatGPT.
- Massive freemium funnel and strong user engagement
- Over 100M MAUs with single-digit percentages converting to paid subscriptions leaves substantial room for ARPU and conversion uplift. Gamification and daily streaks drive habit and retention.
- High-growth, improving profitability profile
- Revenue growth ~40%+ with rising EBITDA margins suggests a long runway of operating leverage as marketing and R&D grow slower than revenue over time.
- AI as a product and cost advantage
- AI powers Duolingo Max (AI conversation simulations, explanations) and content generation, improving learning quality and unit economics over time. Management positions Duolingo as an “AI-first” company, replacing some content creation with AI while scaling courses faster.
- Expansion beyond languages
- New courses in math, music, and chess tap into the broader digital education market and could eventually be monetized similarly to language courses, increasing Duolingo’s addressable market and user engagement per learner.
- Optionality in certification (Duolingo English Test)
- DET is increasingly accepted by universities and offers a high-margin, non-advertising, non-subscription revenue stream that monetizes a different, higher willingness-to-pay segment (international applicants).
Duolingo Bear Case: Key Risks and Challenges
- Competition and commoditization of AI-powered learning
- Language-learning content and AI chatbots are becoming easier to build. Larger players (Big Tech, edtech platforms) could release competing apps using similar AI-powered tutoring, pressuring pricing or engagement.
- Q3 2025 showed bookings dropped from 41% growth last quarter to 33% suggesting revenue softness in upcoming quarters. Management confirmed the slowdown was strategic rather than due to churn or a sudden weakness in conversion. CFO Matt Skaruppa clarified that the shift toward investing in teaching quality and broader user growth initiatives is expected to persist for “several years” and only modestly affect short-term bookings, meaning the company is intentionally prioritizing things like better learning outcomes, AI enhancements, and long-term engagement over next-quarter monetization.
- Engagement quality vs. gamification criticism
- Some educators argue that Duolingo’s focus on streaks and gamification may not translate into deep language proficiency; if this perception grows, institutional adoption or test credibility could be affected.
- Reliance on a single flagship product
- Despite new subjects, Duolingo’s economics remain dominated by language learning. If user growth in languages slows before new verticals scale, overall growth could decelerate.
Duolingo Management Outlook from the Latest Earnings
Based on the most recent earnings updates and shareholder communications (Q2 and Q3 2025): Investing.com+4Duolingo Investors+4Reuters+4
- Growth priorities
- Management continues to emphasize product-led growth, increasing DAUs and conversions to paid, rather than aggressive paid marketing.
- They see continued strong momentum in English and core language courses, with growing contribution from math, music, and chess.
- AI-first strategy
- Duolingo is doubling down on generative AI to:
- Make lessons more adaptive and conversational (Duolingo Max).
- Dramatically accelerate course creation (dozens of new courses launched per year vs. historically ~8/year).
- Reduce content-production costs over time, even though AI costs are currently a modest margin headwind.
- Duolingo is doubling down on generative AI to:
- Financial guidance
- Management has raised 2025 revenue guidance multiple times, now targeting roughly $1.0–1.03B in revenue and high-$200Ms in adjusted EBITDA.
- They highlight strong visibility into bookings and paid subscriber growth, with DAUs and revenue both growing ~40%+ year-to-date.
- Margin outlook
- They expect continued operating leverage, especially in sales & marketing and G&A, while maintaining robust R&D investment.
- AI model costs and expansion into new subjects may cap near-term margin expansion, but the long-term expectation is EBITDA margins in the 30–35% range as the business matures. Barron’s+1
Overall tone: confident but still growth-oriented, with management prioritizing user engagement and product innovation over maximizing near-term margins.
Duolingo TAM and Market Growth (TAM / CAGR)
Duolingo plays in the digital language learning and, increasingly, broader digital education markets.
- Core TAM (digital language learning)
- The digital language learning market is estimated at roughly $29–30B in 2024, expected to grow to about $73B by 2029, implying a ~19–21% CAGR. The Business Research Company+2Grand View Research+2
- Duolingo, with ~$0.75B of 2024 revenue, is still a single-digit percentage share of this market, leaving substantial headroom.
- Broader opportunity
- Management frequently frames a larger opportunity: ~2 billion people worldwide are learning a language in some form. Investors+1
- Expansion into math, music, chess, and potentially other subjects brings Duolingo closer to the multi-hundred-billion-dollar digital education TAM.
For modeling, a reasonable assumption is Duolingo’s core TAM growing ~20% annually, with Duolingo potentially growing faster than the market as it takes share and increases ARPU.
Duolingo Product Portfolio and Revenue Breakdown
Key Products and Services
| Product / Service | Description | Approx. % of 2024 Revenue* | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| Subscriptions (Super & Max) | Paid tiers that remove ads, add features like unlimited “hearts”, offline access, AI tutor | ~81% | Core monetization engine; growing paid subscribers and ARPU. Next Gen Investors+1 |
| Advertising | In-app ads shown to free users | ~7% | Rewarded and interstitial formats integrated into learning loops. Electro IQ+1 |
| Duolingo English Test (DET) | Online English proficiency test for university/immigration purposes | ~6% | 2024 DET revenue ≈ $45–46M; accepted by 4,000+ institutions. Test Resources+1 |
| In-App Purchases / Virtual Goods | Purchases of gems, streak freezes, boosters, cosmetic items | ~5% | Monetizes engaged free users; supports gamification loop. Electro IQ+1 |
| Other (Math, Music, ABC, Chess) | Early-stage education products, children’s literacy app, experimental subjects | ~1% | Currently small but strategically important for long-term expansion. Business of Apps+1 |
*Percentages are approximate, based on 2023–2024 disclosures that subscriptions contribute about 76–83% of revenue, with the remainder from advertising, in-app purchases, and DET.
Duolingo Business Model Explained
Duolingo operates a freemium, product-led growth model with multiple monetization layers: Wikipedia+2AppMakers LA+2
- Free Tier with Ads
- Anyone can use the app for free with ads, limited mistakes (“hearts”), and slower progression.
- This massively broad funnel fuels virality and network effects.
- Subscription Tiers (Super & Max)
- Remove ads and unlock perks like unlimited hearts, progress repair, and personalized practice.
- Max adds AI-powered conversational roleplays and detailed explanations.
- Subscriptions are time-based (monthly / annual), providing recurring revenue.
- In-App Purchases
- Gem packs, streak freezes, power-ups – all non-essential but engagement-boosting.
- Designed to be optional, keeping the core learning experience free.
- Duolingo English Test
- Direct payment from test-takers (primarily international students) for DET.
- High-margin service with low distribution costs; complements the consumer app.
- Optional Enterprise / Institutional
- Limited but growing B2B footprint (schools, universities, organizations) using Duolingo or DET in curricula and admissions.
The growth engine is organic user acquisition via app-store rankings, social virality (especially the Duo mascot), and word of mouth, not heavy paid advertising.
Who Uses Duolingo? Core Customer Segments
- Global Consumer Learners (Free Users)
- Individuals learning languages casually or for travel, work, or personal interest.
- Primarily monetized through ads and, indirectly, as a pool for future conversions.
- Paid Individual Learners
- Users who upgrade to Super or Max for a smoother, faster, ad-free experience.
- Often more serious learners (e.g., professional advancement, long-term hobbyists).
- Students and International Applicants
- Users who take the Duolingo English Test for university admissions or visa processes.
- High willingness-to-pay segment with mission-critical use cases.
- Parents and Children
- Families using Duolingo ABC or early-reading content, plus language learning for kids.
- Institutions and Educators
- Universities accepting DET; some schools and programs integrating Duolingo into curricula or recommending it as a supplemental tool.
Geographically, Duolingo has a strong presence in the US and Europe, but growth is increasingly driven by emerging markets where English proficiency is a key economic lever. Electro IQ+2The Successful Investor Inc+2
Duolingo Competitors and Competitive Landscape
Duolingo competes in a fragmented space of language-learning apps, traditional course providers, and tutoring platforms. Key direct competitors include: Seeking Alpha+1
- Babbel
- Model: Paid subscription language-learning app focused on conversation and practical phrases.
- Overlap: Competes directly with Duolingo in self-paced app-based language learning for adults.
- Differences: More structured, linear courses and stronger emphasis on conversation, but smaller free funnel and less gamification.
- Busuu (a Chegg company)
- Model: Freemium app plus premium subscription; includes community features where learners correct each other’s exercises.
- Overlap: App-based language learning with certificates and some institutional partnerships.
- Differences: Strong social/community component and some CEFR-aligned certificates; smaller scale vs. Duolingo.
- Rosetta Stone (IXL Learning)
- Model: Long-standing language-learning software now offered via subscriptions to consumers, schools, and enterprises.
- Overlap: Competes in structured, multimedia language-learning across many languages.
- Differences: Historically more expensive, less gamified; stronger footprint in schools and corporate training.
Other notable players (not in the top three for this writeup) include Memrise, Busuu competitors like Mondly, and live-tutoring marketplaces such as Preply and italki, which compete more with human instruction than pure app-based learning.
Duolingo Founding History and Company Origins
- Origins (2009–2011)
- The idea for Duolingo came from Luis von Ahn, a Carnegie Mellon professor from Guatemala (also creator of reCAPTCHA), who wanted to make language education free and accessible globally.
- Working with his PhD student Severin Hacker, von Ahn envisioned a platform where users could learn languages while doing useful work for the web. Wikipedia+1
- Company formation and early funding
- Duolingo was founded in 2011 in Pittsburgh, Pennsylvania.
- Early development was supported by von Ahn’s MacArthur “genius” grant and an NSF grant, followed by venture capital from firms including Union Square Ventures and Google Capital. Wikipedia+1
- Product launch and evolution
- The app launched in public beta in 2011 and publicly in 2012, quickly becoming one of the most downloaded education apps on iOS and Android.
- Early monetization experiments (like crowdsourced translation) were eventually replaced with today’s mix of subscriptions, ads, and DET. Wikipedia+1
- IPO and expansion
- Duolingo went public on the NASDAQ (ticker: DUOL) in July 2021, at an implied valuation around $3.7B. Electro IQ+1
- Since the IPO, the company has:
- Scaled to 100M+ MAUs and double-digit millions of paid subscribers.
- Expanded into math, music, and chess.
- Adopted an explicit AI-first strategy, using generative AI for both content and tutoring.
From a research project in a university lab to a global consumer brand with a path toward $1B+ in annual revenue, Duolingo’s history is a classic edtech scale-up story driven by strong product-market fit, freemium distribution, and increasingly, AI-powered learning.
